Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
3. Cycle-by-cycle analysis of resting state data¶
Simulated experiment using the cycle-by-cycle approach.
Say we ran an experiment and want to compare subjects’ resting state data for some reason. Maybe we want to study age, gender, disease state, or something. This has often been done to study differences in oscillatory power or coupling between groups of people. In this notebook, we will run through how to use bycycle to analyze resting state data.
In this example, we have 20 subjects (10 patients, 10 control), and we for some reason hypothesized that their alpha oscillations may be systematically different. For example, we think the patient group should have more top-down input that increases the synchrony in the oscillatory input (measured by its symmetry).
import numpy as np
from scipy import stats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from neurodsp.sim import sim_combined
from neurodsp.filt import filter_signal
from neurodsp.plts import plot_time_series
from bycycle import BycycleGroup
from bycycle.plts import plot_burst_detect_summary, plot_feature_categorical
pd.options.display.max_columns = 10
Load simulated experiment of 10 patients and 10 controls¶
# Simulate experimental data
np.random.seed(0)
n_seconds = 10
fs = 1000
n_subjects = 20
sigs = np.zeros((n_subjects, int(fs * n_seconds)))
for subject_idx in range(n_subjects):
# Manipulate the rise-decay symmetry between the two groups
rdsym = .35 if subject_idx <= int(n_subjects/2) else 0.5
components = {'sim_bursty_oscillation': {'freq': 10, 'enter_burst': .1, 'leave_burst': .1,
'cycle': 'asine', 'rdsym': rdsym},
'sim_powerlaw': {'f_range': (2, None)}}
sigs[subject_idx] = sim_combined(n_seconds, fs, components=components, component_variances=(5, 1))
# Apply lowpass filter to each signal
for idx in range(len(sigs)):
sigs[idx] = filter_signal(sigs[idx], fs, 'lowpass', 30, n_seconds=.2, remove_edges=False)
# Plot an example signal
n_signals = len(sigs)
n_seconds = len(sigs[0])/fs
times = np.arange(0, n_seconds, 1/fs)
plot_time_series(times, sigs[0], lw=2)
Compute cycle-by-cycle features¶
# Frequency band of interest
f_alpha = (7, 13)
# Tuned burst detection parameters
thresholds = {
'amp_fraction': .2,
'amp_consistency': .5,
'period_consistency': .5,
'monotonicity': .9,
'min_n_cycles': 2
}
# Compute features for each signal
bg = BycycleGroup(thresholds=thresholds)
bg.fit(sigs, fs, f_alpha)
# Recompute cycles on edges of bursts with reduced thresholds
bg.recompute_edges(.01)
# Add group and subject ids to dataframes
groups = ['patient' if idx >= int(n_signals/2) else 'control' for idx in range(n_signals)]
subject_ids = [idx for idx in range(n_signals)]
for idx, group in enumerate(groups):
bg.df_features[idx]['group'] = group
bg.df_features[idx]['subject_id'] = subject_ids[idx]
# Concatenate the list of dataframes
df_features = pd.concat(bg.df_features)
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:159: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['amp_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
/Users/ryanhammonds/projects/bycycle/bycycle/burst/utils.py:162: FutureWarning: ChainedAssignmentError: behaviour will change in pandas 3.0!
You are setting values through chained assignment. Currently this works in certain cases, but when using Copy-on-Write (which will become the default behaviour in pandas 3.0) this will never work to update the original DataFrame or Series, because the intermediate object on which we are setting values will behave as a copy.
A typical example is when you are setting values in a column of a DataFrame, like:
df["col"][row_indexer] = value
Use `df.loc[row_indexer, "col"] = values` instead, to perform the assignment in a single step and ensure this keeps updating the original `df`.
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df_features['period_consistency'][cyc_idx] = \
df_features.head()
Confirm appropriateness of burst detection parameters¶
These burst detection parameters seem appropriate because they mostly restrict the analysis to periods of the signal that appear to be bursting. This was confirmed by looking at a few different signal segments from a few subjects.
bg[0].plot(xlim=(0, 10), figsize=(16, 3))
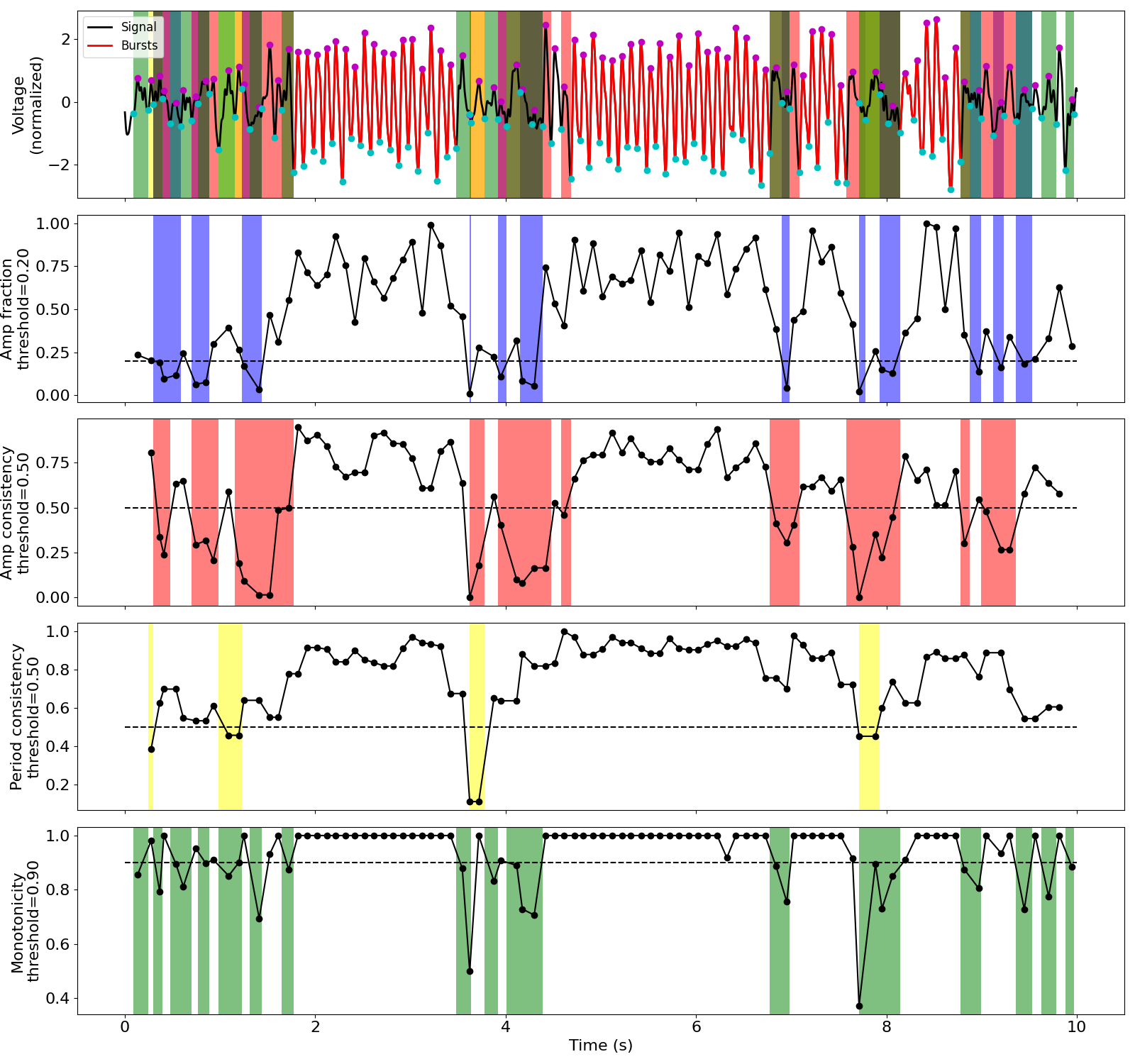
Analyze cycle-by-cycle features¶
Note the significant difference between the treatment and control groups for rise-decay symmetry but not the other features.
# Only consider cycles that were identified to be in bursting regimes
df_features_burst = df_features[df_features['is_burst']]
# Compute average features across subjects in a recording
features_keep = ['volt_amp', 'period', 'time_rdsym', 'time_ptsym']
df_subjects = df_features_burst.groupby(['group', 'subject_id']).mean()[features_keep].reset_index()
df_subjects.head()
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 15), nrows=2, ncols=2)
plot_feature_categorical(df_subjects, 'volt_amp', group_by='group', ax=axes[0][0],
xlabel=['Patient', 'Control'], ylabel='Amplitude')
plot_feature_categorical(df_subjects, 'period', group_by='group', ax=axes[0][1],
xlabel=['Patient', 'Control'], ylabel='Period (ms)')
plot_feature_categorical(df_subjects, 'time_rdsym', group_by='group', ax=axes[1][0],
xlabel=['Patient', 'Control'], ylabel='Rise-Decay Symmetry')
plot_feature_categorical(df_subjects, 'time_ptsym', group_by='group', ax=axes[1][1],
xlabel=['Patient', 'Control'], ylabel='Peak-Trough Symmetry')
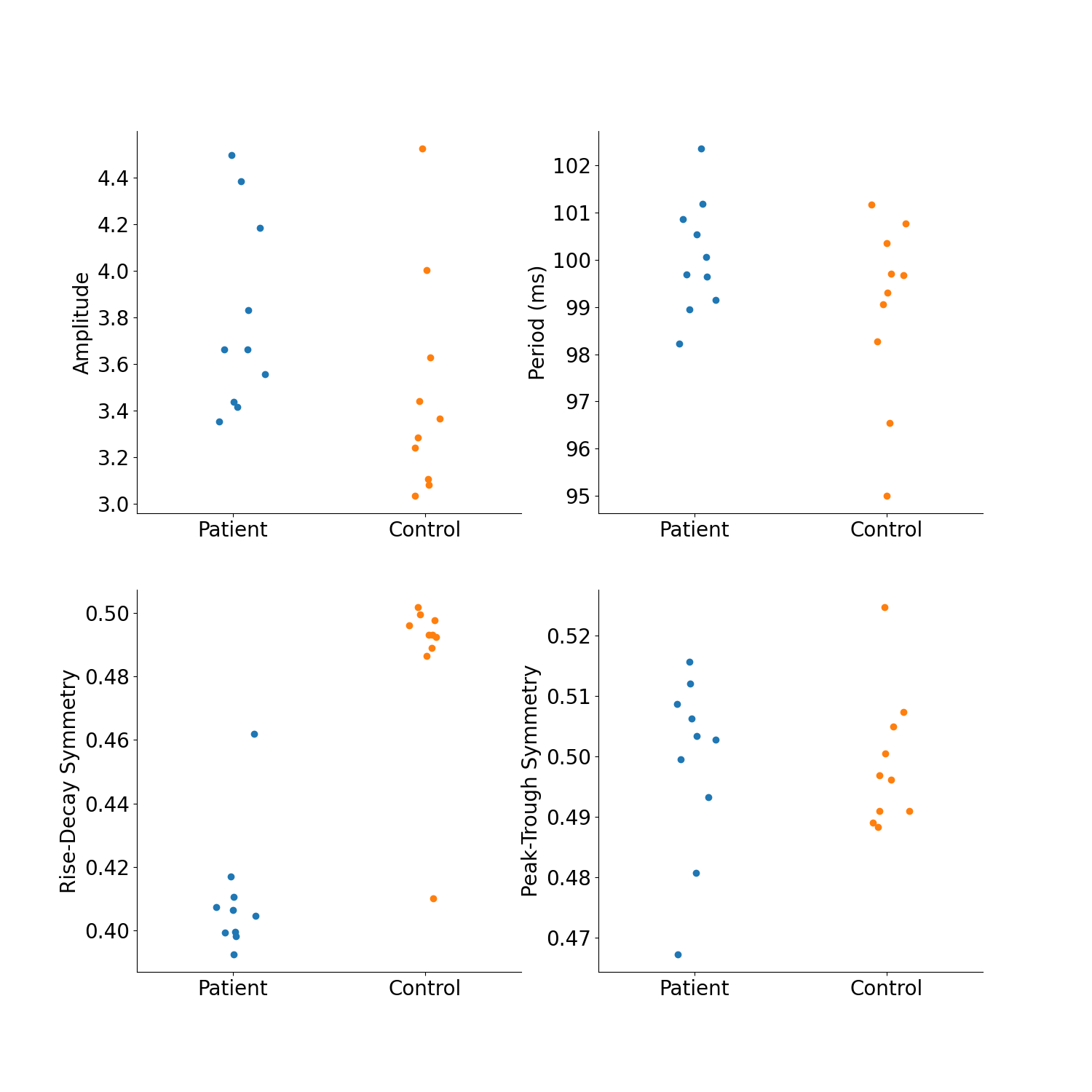
Statistical differences in cycle features¶
feature_names = {'volt_amp': 'Amplitude',
'period': 'Period (ms)',
'time_rdsym': 'Rise-Decay Symmetry',
'time_ptsym': 'Peak-Trough Symmetry'}
for feat, feat_name in feature_names.items():
x_treatment = df_subjects[df_subjects['group'] == 'patient'][feat]
x_control = df_subjects[df_subjects['group'] == 'control'][feat]
ustat, pval = stats.mannwhitneyu(x_treatment, x_control)
print('{:20s} difference between groups, U= {:3.0f}, p={:.5f}'.format(feat_name, ustat, pval))
Amplitude difference between groups, U= 24, p=0.05390
Period (ms) difference between groups, U= 50, p=1.00000
Rise-Decay Symmetry difference between groups, U= 97, p=0.00044
Peak-Trough Symmetry difference between groups, U= 34, p=0.24132
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.636 seconds)